
- #Desktop splunk forwarder trial
- #Desktop splunk forwarder license
i can think of an exception only in systems like containers which you may want to preconfigure each container to make them start sending immediately.Īssuming, your automation will take place in clustered environment, you may want to read little more in Splunk architecture, checking on the commands you have put: One key thing to note, you do monitoring automation with Splunk deployment server in modern systems.
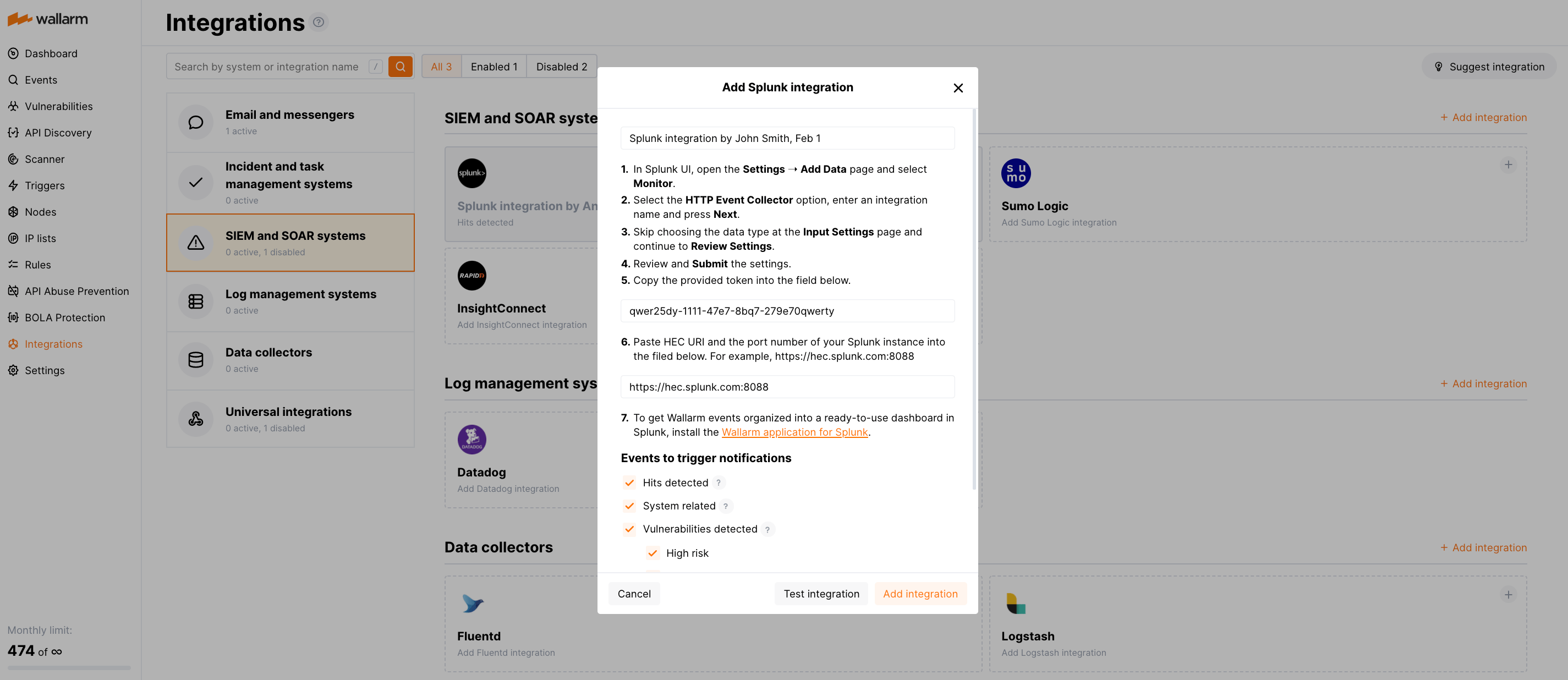
automation via Splunk cli commands (as you have tried in the question). automation via Splunk configuration files. for ansible automation, i guess we can think of 2 strategies, If it is a single instance as I thought, then you can just add from ui. From that point on, whether you have monitors or not, forwarder should be starting its internal logs to Splunk indexer. So if it Universal forwarder, you will be pointing it to your deployment server first, which can deploy nf file into forwarder to tell, where are your indexers are. It seems like you didn't installed Splunk forwarder but Splunk EP single instance. Ideally splunktcp should also get create automatically once I enable the port but it didn't get created and I added it manually. What am I missing as a part of configuration?. Can I use localhost as both Splunk forwarder and indexer which is what I am doing here?. Is my understanding right of separate entry should get created on UI?. My understanding is it should log a separate entry on UI under settings->datainputs for /var/log, right?Īlso, I enabled port 9997 by using following command: splunk enable listen 9997 -auth admin:changeme Now when I am trying following command to add forward-server (indexer) and monitor(data input), i cant see anything on UI.īelow are the commands: splunk add forward-server localhost:9997 -auth admin:changeme I have installed Splunk forwarder on my Red Hat machine (localhost) and I can access Splunk through localhost:8000. I am trying to automate the Splunk forwarder configuration through Ansible but before that I want to try manually through command line. In the Splunk UI, open the Settings menu and click Data Inputs.I am very new to Splunk and have been trying to understand it. For deployments where you set up routing to individual indexes, or you use HEC tokens for RBAC on Splunk, you will create multiple HEC tokens. You need to create at least one HEC token. A HEC endpoint for a paid version of Splunk Cloud on AWS, for a company called "Acme Group," might look like this:Ĭopy the endpoint URL for use when configuring LogStream in the next section. Here are some example URL patterns for HEC endpoints: In Splunk Cloud, identify your HEC endpoint, as described in the Splunk documentation. Using Splunk HEC Identify Your Splunk HEC Endpoint See the Splunk documentation about the compressed setting, and about TLS, which Splunk configuration files still refer to as SSL. 
Do not confuse TLS compression with the compressed setting in the Splunk nf file, which is a different thing, and is for non-TLS connections only. Consider S2S if you plan to route all your data through LogStream first, and you prioritize search performance. This support for concurrent connections is the main advantage of S2S. This helps significantly with Splunk search, by placing a smaller burden on a larger number of indexers. S2S allows each LogStream Worker Process to connect to multiple indexers concurrently, which distributes data very effectively. This provides good load-balancing.Ĭribl generally recommends using Splunk HEC for integrating with Splunk Cloud, because (1) it requires fewer connections than S2S, and therefore consumes less memory and (2) because its superior compression yields lower egress costs. The Splunk HEC endpoints are virtual endpoints, front-ended with load balancers – ELB for AWS, or GLB for GCP. This offers better compression than S2S, which is a binary protocol. Under the hood, it uses the HTTP/S protocol. Using S2S with a BYOL deployment of Splunk.Using S2S with a distributed instance of Splunk.
#Desktop splunk forwarder trial
Using Splunk HEC with the trial version of Splunk.Of all the possible combinations, three have proven most useful in the field: You have a choice of two methods for sending the data:
#Desktop splunk forwarder license
A Bring Your Own License (BYOL) deployment, either in a non-Splunk cloud or on-prem.A distributed Splunk Cloud instance with clustered indexers.The free, single-instance trial version.LogStream can send data to these flavors of Splunk Cloud:






 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
